Research shows that CBD has many proven medical benefits. Most recently, studies focus on the use of CBD for inflammation and, more specifically, hepatitis. The substance shows promising results for both managing conditions and slowing the progression of viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus and can be either acute or chronic. When contracted in adulthood, the virus is typically acute and can last for a few weeks to a few months. Symptoms of acute hepatitis typically develop within six months of transmission. Chronic hepatitis B, on the other hand, develops when the body is unable to rid itself of the virus and is much more severe than acute HBV. Chronic HBV can cause serious health problems, such as liver damage, liver cancer, cirrhosis and even death. Though HPV can become chronic in anyone, persons most at risk are individuals who contract the virus early in life.
Hepatitis B is spread through person-to-person transmission and through semen, blood or other bodily fluids. It cannot be spread through sneezing or coughing. Rather, typical modes of transmission include sexual contact, needle sharing, accidental needle pokes and mother to child transmission.
Symptoms of hepatitis B don’t typically develop until weeks to months after contracting the virus, though some people show signs within two weeks of infection. Other individuals never present symptoms at all. That said, common signs of infection are as follows:
• Weakness and fatigue
• Fever
• Dark urine
• Abdominal pain
• Loss of appetite
• Nausea and vomiting
• Joint paint
• Jaundice
Symptoms can interfere with one’s daily activities and overall quality of life, which is why researchers are constantly on the lookout for ways to better manage them and treat the underlying issue.
For decades, researchers have been attempting to gauge the effectiveness of CBD on inflammation. One group of studies focused on the role of cannabinoid receptors on inflammation. A review of those studies concluded that the activation of CB2 receptors by cannabinoids, either in vivo or in vitro, helps to decrease the activation rate of inflammatory cells. More notable findings suggest that, in addition to reducing inflammation, CBD can help slow the progression of certain diseases, such as the HBV virus.

Explore this cbd consumption methods tutorial and follow the step-by-step process to select, use, and verify the safest ways to consume CBD for wellness.
Read More
Learn what CBD edibles are, their main types, expected effects, legal status, safety factors, and how they compare to other forms of CBD.
Read More
Therapeutic Uses of CBD Managing Chronic Pain with CBD Struggling with chronic pain? CBD might help. Studies suggest it can reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort,...
Read More
Just as CBD may help humans due to its interaction with the body’s endocannabinoid system, the same is true of dogs. CBD has the potential...
Read More
Cannabis has been used for millennia to treat numerous health conditions. Current research offers promising results on the effects of CBD oil on breast cancer.
Read More
What Is CBD for Cats? CBD (Cannabidiol) is a natural compound from hemp. It’s non-psychoactive, meaning your cat won’t get “high.” Instead, it works with...
Read More
1. Understanding Neuropathic Pain Neuropathic pain results from nerve damage or dysfunction, causing symptoms like burning, tingling, or sharp shooting pains. Common Causes: Symptoms Include:...
Read More
CBD for Pets: A Pet Parent’s Guide to Dosage We all want the best for our pets, especially when they’re struggling with pain, anxiety, or...
Read More
What Is Lupus? Lupus is a long-term autoimmune condition that can impact multiple organs, including the skin, heart, lungs, and kidneys. The most common type...
Read More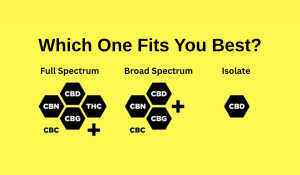
1. Full-Spectrum CBD: The All-In-One Option What it is: Contains CBD, minor cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids — and less than 0.3% THC. Why choose it: Promotes...
Read More