You’ve probably heard of THC, but what about its lesser-known THCA? Yeah, it can be confusing but don’t worry we will explain everything here. Let’s jump in!
THCA Explained: The Basics THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a big player in the cannabis world. But what is it? Let’s dig into the weeds, so to speak.
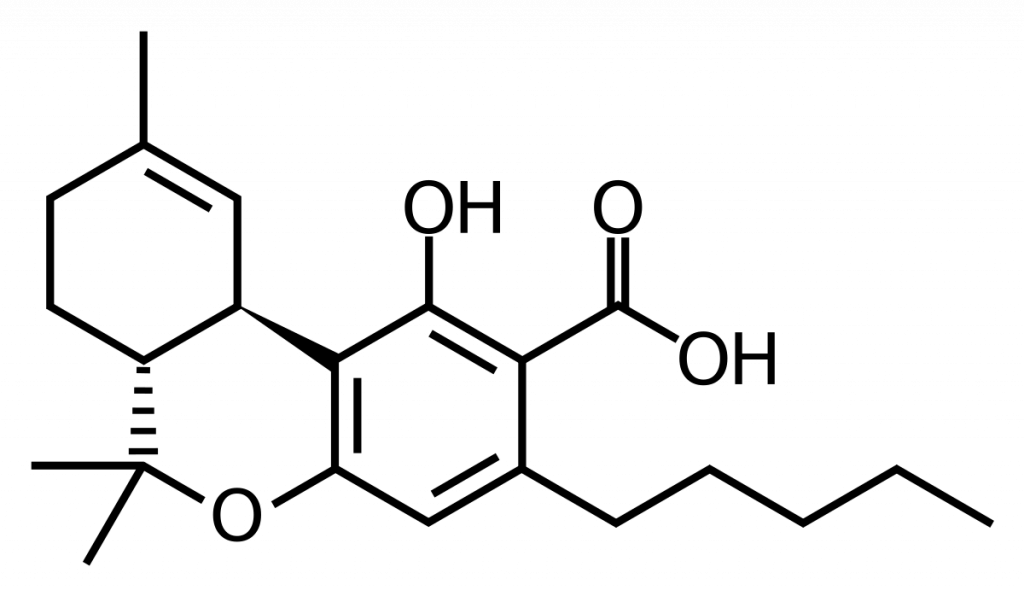
THCA is like the caterpillar to THC’s butterfly. It’s the precursor, the starting point. In scientific terms, it’s a carboxylic acid form of THC. Imagine THCA as a shy kid at a party. It’s there, but it’s not really interacting with anyone. That extra carboxyl group almost like a big bulky backpack that keeps it from mingling.
Here’s a fun fact: when cannabis is growing, it doesn’t actually produce THC, it makes THCA instead. THCA is found in the trichomes of the plant. These are those tiny, crystal-like structures that make cannabis buds look frosty.

Not all cannabis is created equal when it comes to THCA content. Factors like genetics, growing conditions, and harvest time all play a role in THCA content and dosage. It’s like how some apple trees produce sweeter fruit than others. Same idea, but with cannabinoids instead of sugar.
Remember how we said THCA doesn’t get you high, but THC does? Here’s the process.
Essentially, it’s what happens when you apply heat to THCA. Think of it like popcorn. You start with kernels (THCA), apply heat, and poof! You get THC. The heat causes THCA to lose its carboxyl group, transforming it into THC.
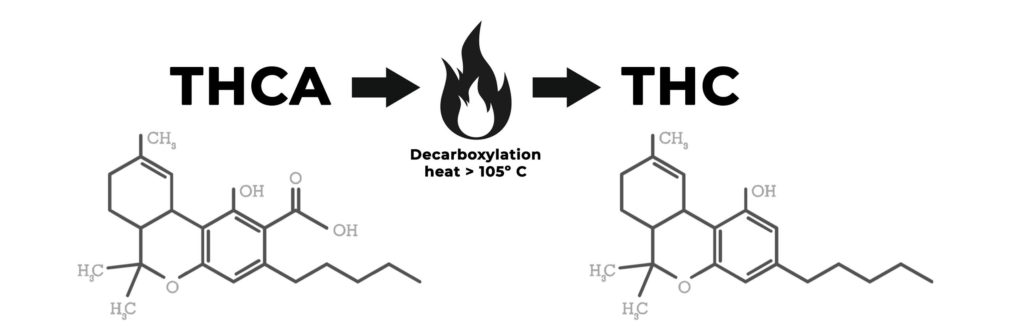
The THCA to THC conversion isn’t just about heat. Time plays a role too. Even at room temperature, THCA slowly converts to THC over time. Other factors like light exposure and oxygen can speed up the process. It’s like how an apple left on the counter will eventually turn brown. THCA is always slowly changing, even if you can’t see it.
What is the benefit of THCA if it does not give you psychoactive “high”? Is there a medical benefit?
The list of potential THCA benefits are prevalent. Some research points to anti-nausea effects, appetite stimulation, and even anti-cancer properties. But let’s not get excited too fast.
So, you’re intrigued by THCA. How do you actually use it?
Can you eat raw cannabis? Raw cannabis is full of THCA and it’s edible. Some folks add raw cannabis leaves to salads or smoothies. It’s like adding a super-spinach to your diet. But it’s an acquired taste, and may take time to develop tolerance for your palate.
THCA crystalline is almost pure THCA, looking like little diamonds and the crystals can be added to food or drinks. It is like adding another layer of excitement in your food. An important reminder, heat will convert it to THC.
Cannabis juicing is a way to get a concentrated dose of THCA without the psychoactive effects. Imagine a green juice, but instead of kale, it’s cannabis. It’s not for everyone, but there are some experience much benefits.

The legal landscape around cannabis is… complicated. And THCA adds another layer to that complexity due to state and federal regulation that are not clearly defined.
Here’s where things get tricky. Federally, THCA is in a gray area. It’s not specifically scheduled like THC is. But state laws vary wildly. In some places, THCA is treated just like THC. In others, it’s more of a “don’t ask, don’t tell” situation. Always check your local laws before experimenting with THCA.
Thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp-derived products are legal federally. This has led to a boom in hemp-derived THCA products. But the legal status of these products is still not well defined. You are at a mercy of interpretation of attorneys and regulators.
The medical world is starting to take notice of THCA. Here’s what’s happening in the lab.
There are promising studies that may redefine our health in the near future. Such as studies have looked at THCA for conditions ranging from epilepsy to metabolic disorders and neurodegenerative diseases to chronic pain. It’s like scientists have found a new toy, and they’re figuring out potential benefits to mankind and animals.
No, THCA by itself won’t get you high. It needs to be converted to THC through heat (like smoking or vaping) or over time to have psychoactive effects.
The legal status of THCA is complicated and varies by location. In some places, it’s treated the same as THC, while in others, THCA derived from hemp might be considered legal. Always check your local laws.
THCA can be consumed in raw cannabis, as crystalline extracts, or in juices and smoothies made from raw cannabis. Remember, heating THCA will convert it to THC.
Early research suggests THCA might have anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-nausea properties. However, more studies are needed to confirm these effects.
While THCA itself isn’t typically tested for, there’s a small chance it could convert to THC in your body or during testing. If you’re concerned about drug tests, it’s best to avoid all cannabis products.
THCA and CBD are different cannabinoids with distinct properties. While neither is psychoactive like THC, they interact with the body in different ways and are being studied for different potential benefits.
Does THCA Show Up in Drug Tests? The question of whether THCA shows up in drug tests is nuanced and depends on several factors. THCA...
Read More
Rising Popularity in the Cannabis Industry The popularity of THCA carts is on the rise in the cannabis industry. This growth can be attributed to...
Read More
A THCA vape is a device used to vaporize THCA-rich cannabis extracts. These vapes heat the THCA just enough to create vapor, but not so...
Read More
The cannabis plant contains over 100 different cannabinoids, each with its unique properties and effects. Among these, THCA and Delta 9 THC stand out due...
Read More
What Are THCA Diamonds? Chemical Composition and Structure THCA diamonds are pure, crystalline forms of THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid). They look like little transparent crystals, kind...
Read More
Understanding THCA: A Primer Before we start our local THCA treasure hunt, let’s make sure we’re on the same page about how is it Different...
Read More
THCA vs THC: A Molecular Comparison At first glance, THCA and THC might seem like twins. But look closer, and you’ll see they’re more like...
Read More
The Potential Benefits of THCA Before diving into the side effects, it’s worth noting that THCA has shown potential benefits in preliminary studies: Anti-inflammatory Properties...
Read More
THCA Flower At its core, THCA flower refers to cannabis buds that contain high levels of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), the non-psychoactive precursor to THC. These...
Read More
Introduction to THCA Definition of THCA as a Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoid Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid (THCA) is a prominent cannabinoid found in raw cannabis plants. Unlike Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC),...
Read More