As research into this complex plant continues, we’re uncovering more about its various compounds and their effects on the human body. Two such compounds that often come up in discussions are THCA and Delta 9 THC. But what exactly are they, and how do they differ? Let’s dive into the world of cannabinoids and explore the key differences between THCA and Delta 9.
The cannabis plant contains over 100 different cannabinoids, each with its unique properties and effects. Among these, THCA and Delta 9 THC stand out due to their prevalence and the interest they’ve generated in both medical and recreational contexts.
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is often referred to as the “raw” or “acidic” form of THC. It’s the compound found in fresh, unheated cannabis plants. Here are some key points about THCA:
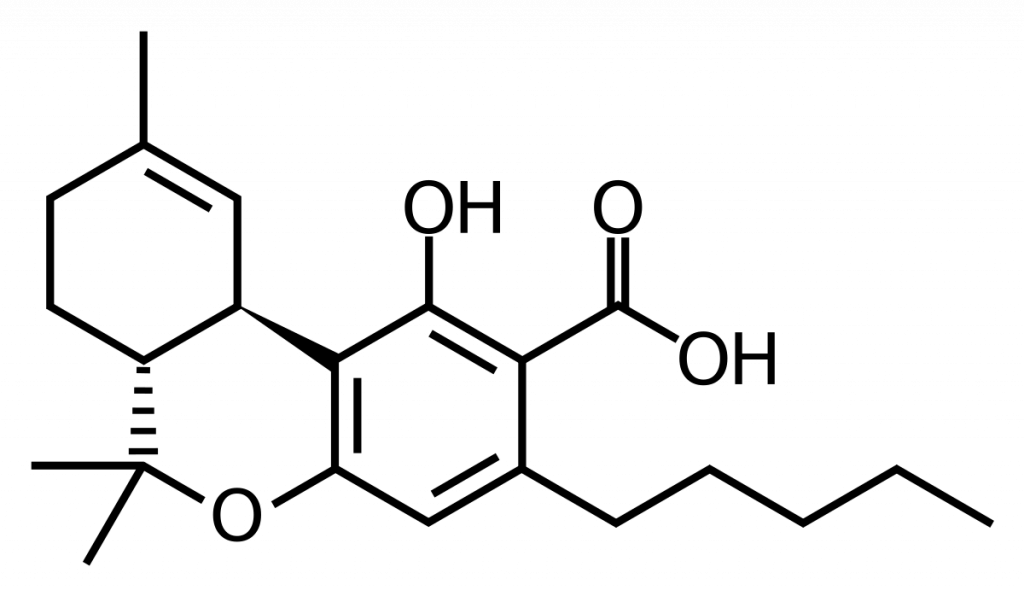
THCA is gaining attention in the wellness community for its potential health benefits without the intoxicating effects associated with THC. Some people are incorporating raw cannabis into their diets, juicing cannabis leaves, or using THCA-rich products for their potential therapeutic effects.
Delta 9 THC, or simply THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. It’s responsible for the “high” people experience when consuming marijuana. Here’s what you need to know about Delta 9 THC:
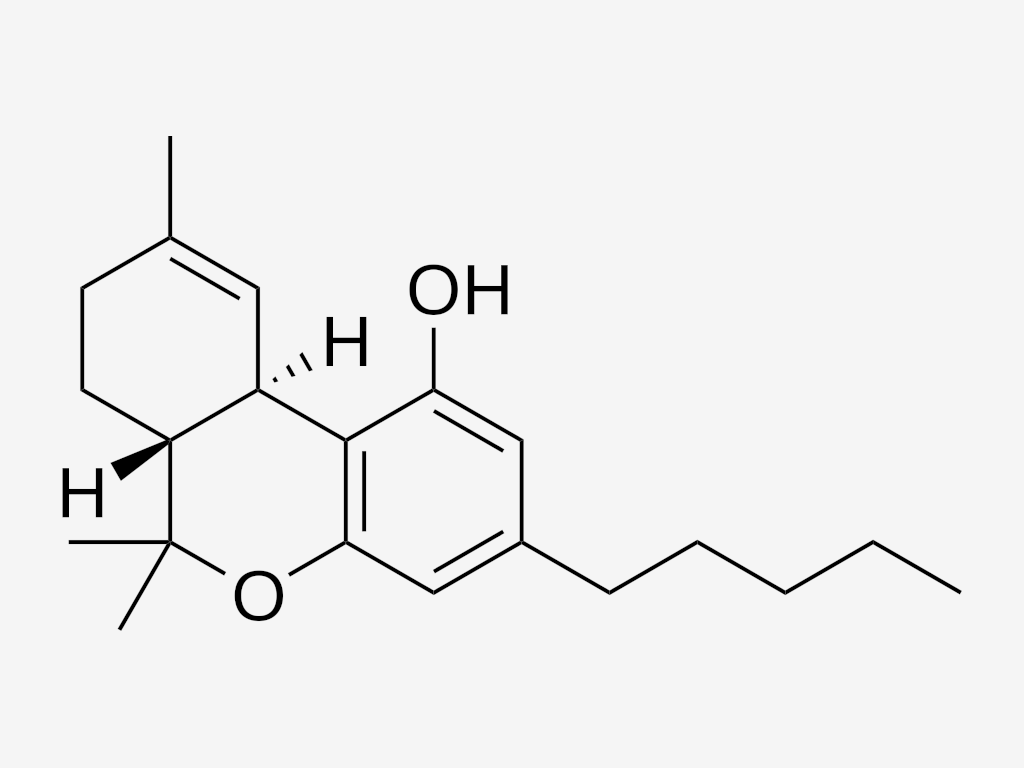
Delta 9 THC has been the subject of extensive research due to its profound effects on the human body and mind. It’s used both recreationally and medicinally, with potential applications in pain management, appetite stimulation, and nausea control.
One of the most fascinating aspects of the relationship between THCA and Delta 9 THC is the conversion process that links them. This process is called decarboxylation, and it’s crucial to understanding how these compounds interact with our bodies.
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that occurs when THCA is exposed to heat. This process removes a carboxyl group from the THCA molecule, transforming it into Delta 9 THC. Here’s how it works:
This conversion is why raw cannabis doesn’t produce a high, but smoking or baking it does. It’s also why many cannabis products are heated or “”activated”” during production to increase their THC content.
The effects of THCA and Delta 9 THC are strikingly different, primarily due to how they interact with our endocannabinoid system:
THCA:
Delta 9 THC:
The onset and duration of effects also differ. THCA’s effects are generally subtler and may be more cumulative over time, while Delta 9 THC’s effects are typically felt quickly and last for several hours.
Both THCA and Delta 9 THC have garnered interest in the medical community for their potential therapeutic applications:
THCA in therapeutics:
Delta 9 THC in medicine:
Some researchers believe that the combination of various cannabinoids, including THCA and Delta 9 THC, may produce enhanced therapeutic effects. This concept, known as the “”entourage effect,”” suggests that the compounds in cannabis work best together rather than in isolation.
The legal status of THCA and Delta 9 THC is complex and varies depending on jurisdiction:
It’s crucial to check local laws before using or possessing any cannabis-derived products, as regulations can vary significantly between locations.
The ways people consume THCA and Delta 9 THC differ due to their distinct properties:
THCA consumption:
Delta 9 THC consumption:
The choice of consumption method can significantly affect the onset, duration, and intensity of effects, particularly for Delta 9 THC.
While both compounds are generally considered to have a good safety profile, they’re not without potential risks:
THCA potential risks:
Delta 9 THC side effects:
It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using any cannabis products, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications.
For those subject to drug testing, it’s important to understand how THCA and Delta 9 THC might affect test results:
It’s crucial to be aware of these implications, especially in contexts where drug testing is common, such as employment or athletics.
The entourage effect is a theory suggesting that cannabis compounds work synergistically, potentially enhancing their individual effects. In the context of THCA and Delta 9 THC:
The field of cannabinoid research is rapidly evolving, with ongoing studies exploring the potential of both THCA and Delta 9 THC:
As research progresses, we may discover new applications and gain a deeper understanding of how these cannabinoids interact with our bodies.
THCA itself is non-psychoactive and won’t produce a high. However, if THCA is exposed to heat, it converts to THC, which can cause psychoactive effects.
The legality of Delta 9 THC varies by location. It’s federally illegal in the US but legal for medical or recreational use in many states. Always check local laws.
While THCA itself typically doesn’t show up on drug tests, there’s a possibility it could convert to THC in the body or during testing, potentially leading to a positive result.
Both compounds are being studied for various conditions, including chronic pain, inflammation, nausea, and neurodegenerative diseases. However, more research is needed to fully understand their potential benefits.
The duration of Delta 9 THC effects can vary based on factors like dosage and consumption method, but typically last 2-6 hours when smoked or vaped, and up to 12 hours or more when consumed as an edible.
While it’s possible to convert THCA to Delta 9 THC through decarboxylation (heating), it’s not recommended to attempt this at home due to legal and safety concerns.
Does THCA Show Up in Drug Tests? The question of whether THCA shows up in drug tests is nuanced and depends on several factors. THCA...
Read More
What is Limonene? Limonene is a naturally occurring aromatic compound that belongs to the family of terpenes. Terpenes are organic compounds produced by a variety...
Read More
What Does the Terpene Caryophyllene Do? Caryophyllene, a unique sesquiterpene found in various plants including cannabis, black pepper, and cloves, stands out for its ability...
Read More
Presence in Cannabis and Other Plants Terpenes are abundantly present in cannabis, alongside other plants like mint, lemon, and pine. In cannabis, terpenes enrich the...
Read More
Rising Popularity in the Cannabis Industry The popularity of THCA carts is on the rise in the cannabis industry. This growth can be attributed to...
Read More
A THCA vape is a device used to vaporize THCA-rich cannabis extracts. These vapes heat the THCA just enough to create vapor, but not so...
Read More
Chemical Structure and Properties THCA is like the caterpillar to THC’s butterfly. It’s the precursor, the starting point. In scientific terms, it’s a carboxylic acid...
Read More
What Are THCA Diamonds? Chemical Composition and Structure THCA diamonds are pure, crystalline forms of THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid). They look like little transparent crystals, kind...
Read More
Understanding THCA: A Primer Before we start our local THCA treasure hunt, let’s make sure we’re on the same page about how is it Different...
Read More
THCA vs THC: A Molecular Comparison At first glance, THCA and THC might seem like twins. But look closer, and you’ll see they’re more like...
Read More